📂 View the code on GitHub
ANPR Image Preprocessing: Step-by-Step Guide
This article demonstrates the key image preprocessing steps for Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems. We’ll walk through each step with practical examples and visualizations.
Outline:
- Import Required Libraries
- Load and Display the Input Image
- Convert Image to Grayscale
- Apply Gaussian Blur
- Perform Edge Detection
- Apply Morphological Operations
- Find and Draw Contours
1. Import Required Libraries
We start by importing the essential libraries for image processing and visualization.
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# For notebook display
%matplotlib inline2. Load and Display the Input Image
Let’s load a sample number plate image and display it. In a real-world scenario, you would replace the image path with your own vehicle image.
# Load the image (replace with your image path)
image_path = './sample_images/sample_plate.jpg'
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if image is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Image not found at {image_path}. Please check the path.")
# Convert BGR (OpenCV default) to RGB for Matplotlib display
image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(image_rgb)
plt.title('Original Input Image')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()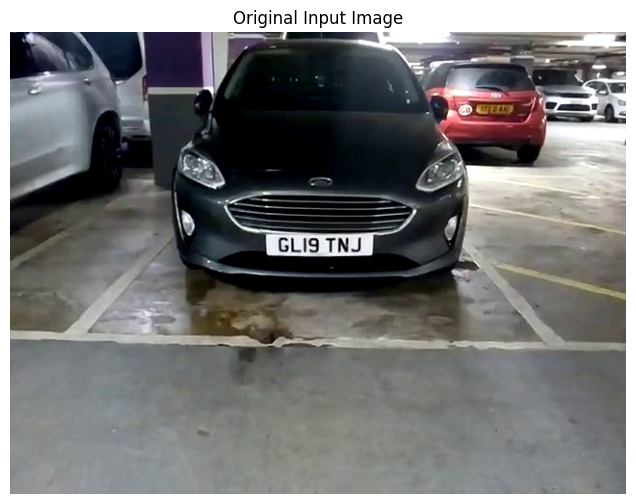
3. Convert Image to Grayscale
Converting to grayscale is a crucial first step that simplifies processing and reduces computational complexity while preserving essential structural information.
# Convert the image to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(gray, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Grayscale Image')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()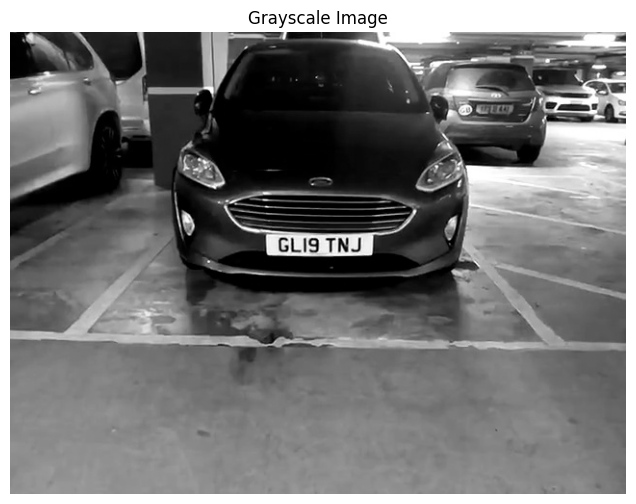
4. Apply Gaussian Blur
Gaussian blur helps reduce image noise and smooths out details, making subsequent edge detection more robust and reliable.
# Apply Gaussian blur to the grayscale image
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(blurred, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Blurred Image (Gaussian Blur)')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()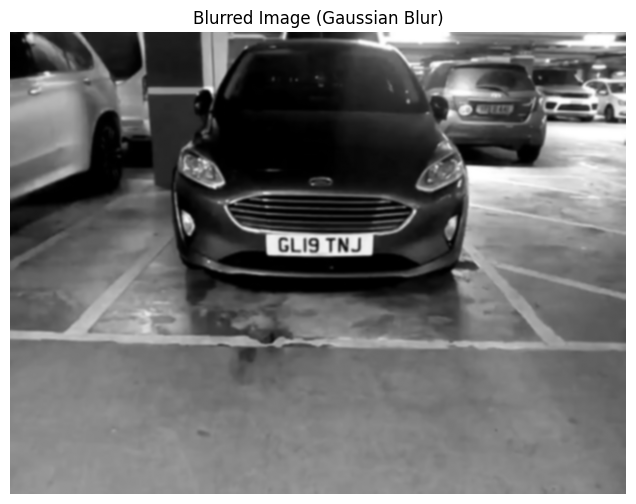
5. Perform Edge Detection
Edge detection using the Canny algorithm highlights boundaries and contours in the image, which is essential for identifying the number plate region.
# Perform Canny edge detection
edges = cv2.Canny(blurred, 100, 200)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(edges, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Edge Detection (Canny)')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()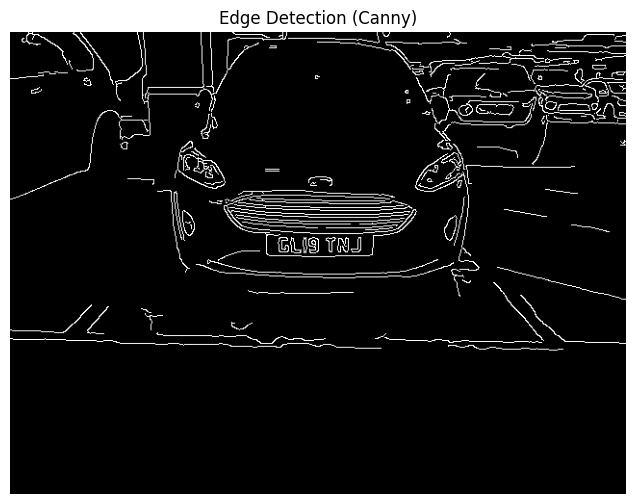
6. Apply Morphological Operations
Morphological transformations like dilation and erosion help enhance edges and close gaps, making contour detection more effective.
# Define a kernel for morphological operations
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
# Apply dilation followed by erosion (closing)
dilated = cv2.dilate(edges, kernel, iterations=1)
eroded = cv2.erode(dilated, kernel, iterations=1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(eroded, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Morphological Operations (Dilation + Erosion)')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()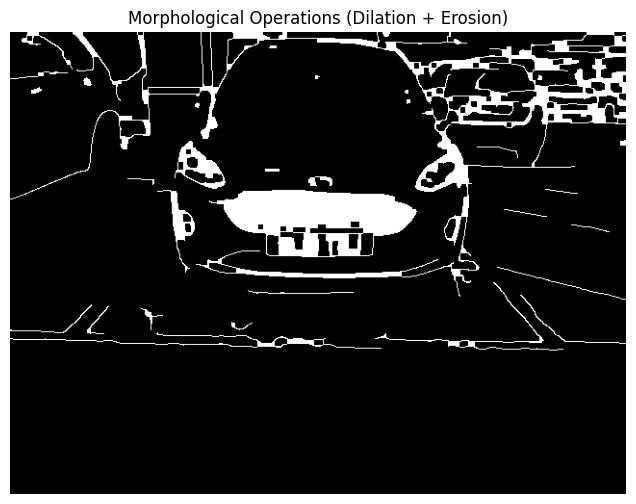
7. Find and Draw Contours
Finally, we identify contours in the processed image to locate potential number plate regions. Contours represent the boundaries of objects and are crucial for plate localization.
# Find contours in the processed image
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(eroded, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Draw contours on a copy of the original image
contour_img = image_rgb.copy()
cv2.drawContours(contour_img, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(contour_img)
plt.title('Contours Detected')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
print(f"Number of contours found: {len(contours)}")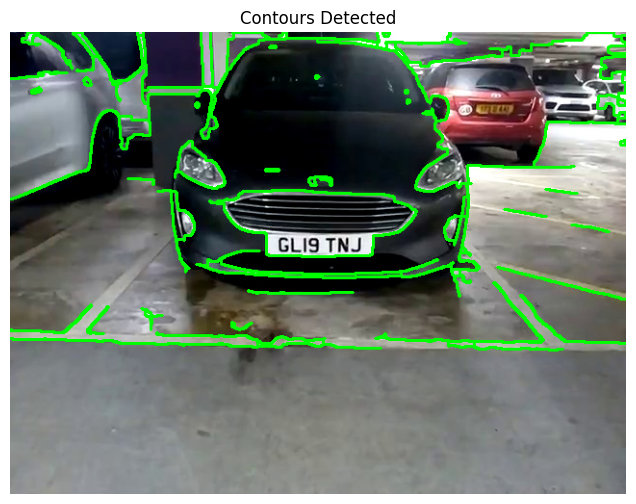
Conclusion
This preprocessing pipeline forms the foundation of any robust ANPR system. Each step serves a specific purpose:
- Grayscale conversion reduces complexity while preserving structural information
- Gaussian blur removes noise and smooths the image
- Edge detection highlights important boundaries
- Morphological operations enhance and connect edge features
- Contour detection identifies potential regions of interest
The next step in building an ANPR system would be to filter these contours based on geometric properties (aspect ratio, area, etc.) to identify the most likely number plate candidates.
For more advanced techniques and the complete ANPR pipeline, check out the other articles in this series covering plate detection, character segmentation, and OCR recognition.